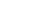
A short overview of the Anti-Atlas, Morocco
DR.Hervé Rezeau, DR.Cyril Chelle-Michou & DR.Michael Calder
SEG Student Chapter of Geneva (Switzerland)
SEG Student Chapter of Montpellier (France)
INTRODUCTION
Geology of Morocco has been subdivided into four structural domains, from north to south they are the following: the Rif domain, the Meseta domain, the High Atlas, and the Anti-Atlas, as they are shown in (Figure 1).
The Rif Range extends along the Mediterranean coast from the Kabylian-Tellian belts up to the Strait of Gibraltar. South of it, the Meseta domain is located, where elevated plateaus and intramontane basins occur. Further south the High Atlas system is found, which displays several massifs close to 4000 m, including the highest peak of northern Africa (Jebel Toubkal). The Middle Atlas represents a branch of the Atlas system that extends obliquely across the Meseta domain, and exceeds 3000 m in elevation. Finally, the Anti-Atlas domain is found, which rises forming a massive mountain that achieves up to 2700 m. Further south the elevation decreases both southward and westward from ca. 1000 m to less than 200 m close to the Atlantic.
Figure 1: Elevation map of Morocco and neighbouring countries from GTOPO30 database (A. Michard et al. 2008)
GEOLOGICAL SETTING OF THE ANTI-ATLAS
The Anti-Atlas mountain belt is located in the northern part of the West African Craton (WAC). It is stretching NE-SW and is characterized by Precambrian to late Proterozoic rocks covered by younger sediments of Edicaran to Cambrian in age. The geological boundary between the Anti-Atlas and High Atlas is structurally marked by the South Atlas fault (SAF) (Fig.2). The Anti-Atlas massif is a zone of wide domal uplift with much weaker Alpine age deformation. The volcanics and conglomerates rocks from the Ouarzazate & Bou Salda group in the North-East are surrounding the older volcanics rocks
The Anti-Atlas mountain belt is located in the northern part of the West African Craton (WAC). It is stretching NE-SW and is characterized by Precambrian to late Proterozoic rocks covered by younger sediments of Edicaran to Cambrian in age. The geological boundary between the Anti-Atlas and High Atlas is structurally marked by the South Atlas fault (SAF) (Fig.2). The Anti-Atlas massif is a zone of wide domal uplift with much weaker Alpine age deformation. The volcanics and conglomerates rocks from the Ouarzazate & Bou Salda group in the North-East are surrounding the older volcanics rocks and turbidite sequences from the Sahgro Group and the Pan-African granite intrusions. This geomorphological feature is commonly called inliers (“boutonnière” in French) and is the result of an exposed older rock formation surrounded by younger rock, and is due to a high erosion rate of rocks with different hardness but also encouraged by deformation such as folding and faulting (Gasquet et al. 2005). Several slivers of ophiolites are present in the Anti-Atlas belt, the best preserved are situated in the Bou Azzer, Siroua and Iriri region, which represent remnant of an ocean closure. The basement is composed of schists, granites and mylonites of Paleoproterozoic age. The latest Variscan and Alpine orogenic events overprint most of the Anti-Atlas geological province and thus complicate the Pre- Cambrian geodynamic interpretation. However, two main periods of tectono-thermal magmatic activity (Gasquet et al. 2005) are now recognised :
(i)A Palaeoproterozoic period, corresponding to the Eburnean (Birimian) orogeny,
(ii)A Neoproterozoic period, corresponding to the Pan-African orogeny.
Figure 2: Schematic map of the Anti-Atlas Precambrian inliers (Boutonnière), and location of the maps, satellite views and lithospheric profile presented hereafter (Gasquet et al. 2008)
Source web : DR.Hervé Rezeau, DR.Cyril Chelle-Michou & DR.Michael Calder unige.ch
Les articles en relation

Les premiers animaux étaient peut-être des éponges
Les premiers animaux étaient peut-être des éponges Reconstituer l'origine des animaux, et en particulier sous formes multicellulaires, est l'une des clés permettant de déterminer notre origin
Savoir plus...
COP 23 : où en est l'accord de Paris ?
COP 23 : où en est l'accord de Paris ? À Bonn, en Allemagne, vient de s'ouvrir la « Conférence des parties » numéro 23, avec les États-Unis en vedette surréaliste, pr&eacu
Savoir plus...
Patrimoine culturel matériel
Patrimoine culturel matériel Le Maroc a ratifié la convention du Patrimoine Mondial et a été élu membre du comité du patrimoine mondial en 1995 et membre du bureau du patrimoine mondial en 19
Savoir plus...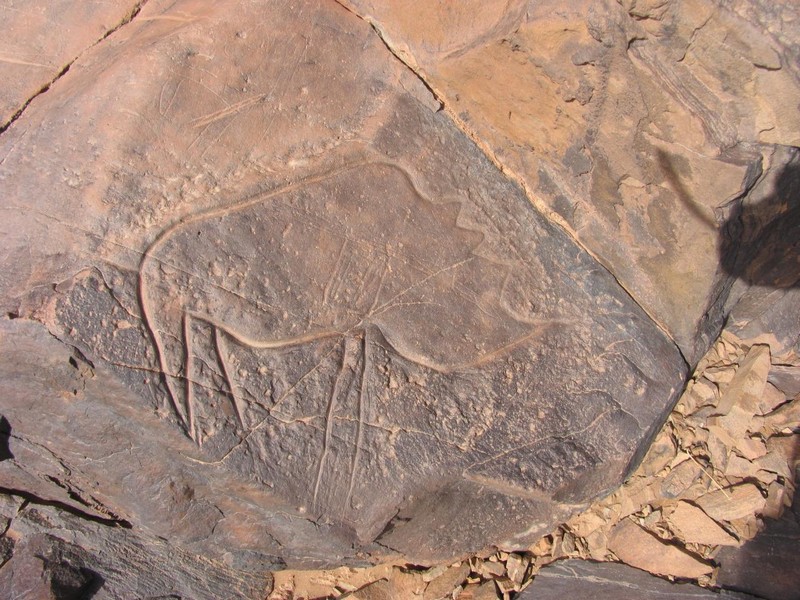
Maroc : Appel pour la préservation des sites rupestres dans la région de Tata
Maroc : Appel pour la préservation des sites rupestres dans la région de Tata Les travaux d’une rencontre tenue, récemment à Tata, sur la préservation des sites rupestres de la province ont &e
Savoir plus...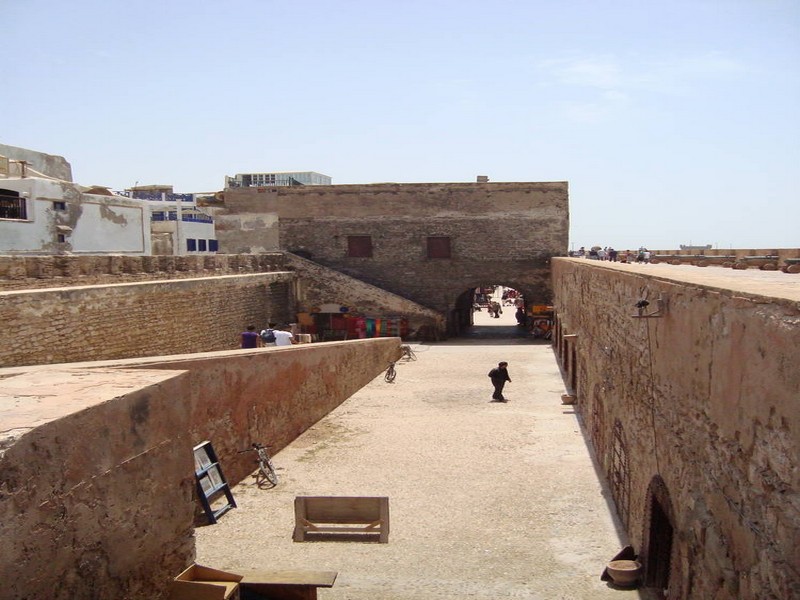
Médina d’Essaouira (ancienne Mogador)
Médina d’Essaouira (ancienne Mogador) Essaouira est un exemple exceptionnel de ville fortifiée de la fin du XVIIIe siècle, construite en Afrique du Nord selon les principes de l'architecture militaire e
Savoir plus...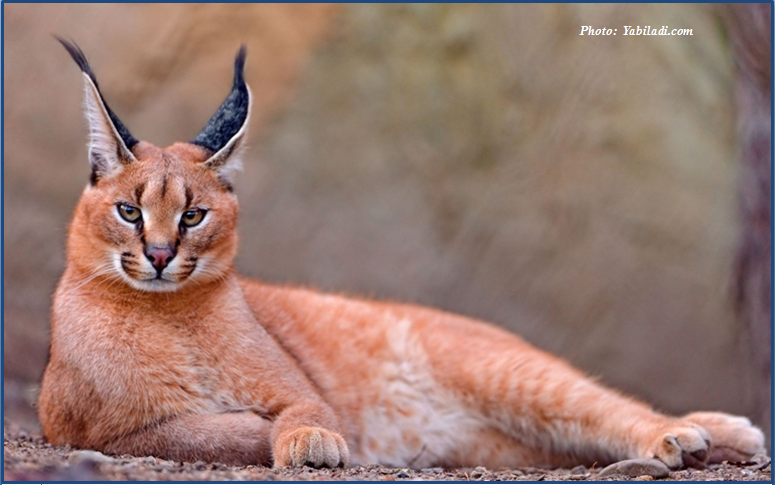
Mrirt: observation d’un caracal
Mrirt: observation d’un caracal Un ornithologue marocain a observé un caracal à l’état sauvage, la semaine dernière, dans la région de Mrirt. Encore une de ces nouvelles qu’on aime. L
Savoir plus...
Artisanat: Tarfaya à l’heure de son Salon régional
Artisanat: Tarfaya à l’heure de son Salon régional Le Salon régional de l’artisanat de Tarfaya a été inauguré mardi avec la participation d’exposants venus des diff&ea
Savoir plus...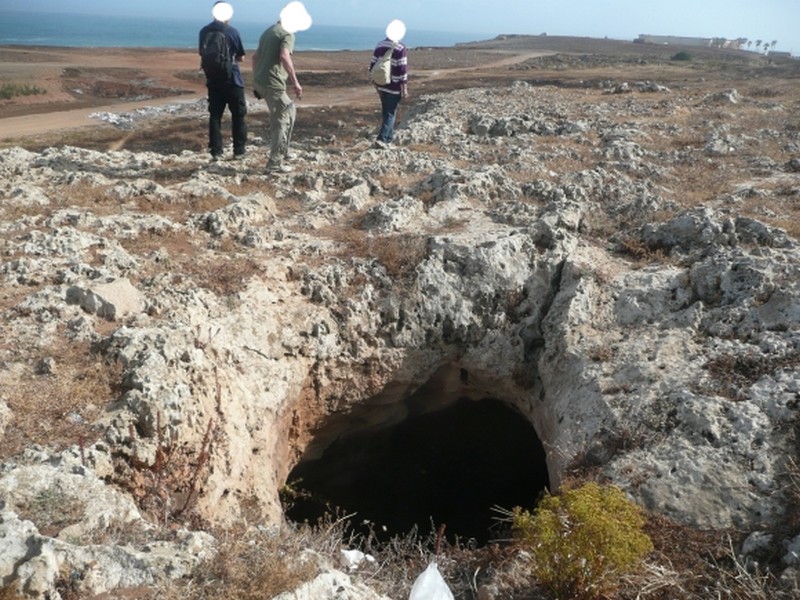
La grotte de Dares Soltan 1 dans son contexte archéologique et géomorphologique
La grotte de Dares Soltan 1 dans son contexte archéologique et géomorphologique 1. Intérêt scientifique : La grotte de Dar es-Soltan 1 fait partie d’un ensemble d’abris sous roche ouver
Savoir plus...
Les épinards rendent-ils vraiment plus costaud ?
Les épinards rendent-ils vraiment plus costaud ? « Mange tes épinards, si tu veux devenir fort ! » Enfant, nous avons tous entendu cette recommandation. Mais notre maman savait-elle r&ea
Savoir plus...
LA CAPACITE GEO-TOURISTIQUES DES REGIONS DE L’ANTI ATLAS DU JBEL BANI
LA CAPACITE GEO-TOURISTIQUES DES REGIONS DE L’ANTI ATLAS DU JBEL BANI Le Sud Maroc, particulièrement, le territoire Sous Sahara Atlantique, Guelmim Oued Noun et le Grand Sud Maroc ont lancé de gros chantiers pour
Savoir plus...Les tags en relation
En savoir plus sur " Géologie et TSGJB - AMDGJB "
Consulter les vidéos de " Géologie et TSGJB - AMDGJB " Consulter les photos de " Géologie et TSGJB - AMDGJB " Consulter les publications de " Géologie et TSGJB - AMDGJB " Consulter les éditions de " Géologie et TSGJB - AMDGJB " Consulter les communications de " Géologie et TSGJB - AMDGJB "Recherche du site
Recherche avancée / Spécifique
Géoparc et Recherche Scientifique
Le coins de l’étudiant



Blog Géoparc Jbel Bani
Dictionnaire scientifique
Plus de 123.000 mots scientifiques
Les publications
Géo parc Jbel Bani

Circuits & excursions touristiques
cartothéques


Photothéques
Publications & éditions